An SSA–RF-based Lunar Surface Rock Abundance Retrieval Method Using Multi-source Remote Sensing Data
Published in Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2025
Recommended citation: Z. Guo, Z. Song, C. Li, G. Shu, and N. Li. "An SSA–RF-based Lunar Surface Rock Abundance Retrieval Method Using Multi-source Remote Sensing Data". Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics. 2025, 26, 2, 025005.
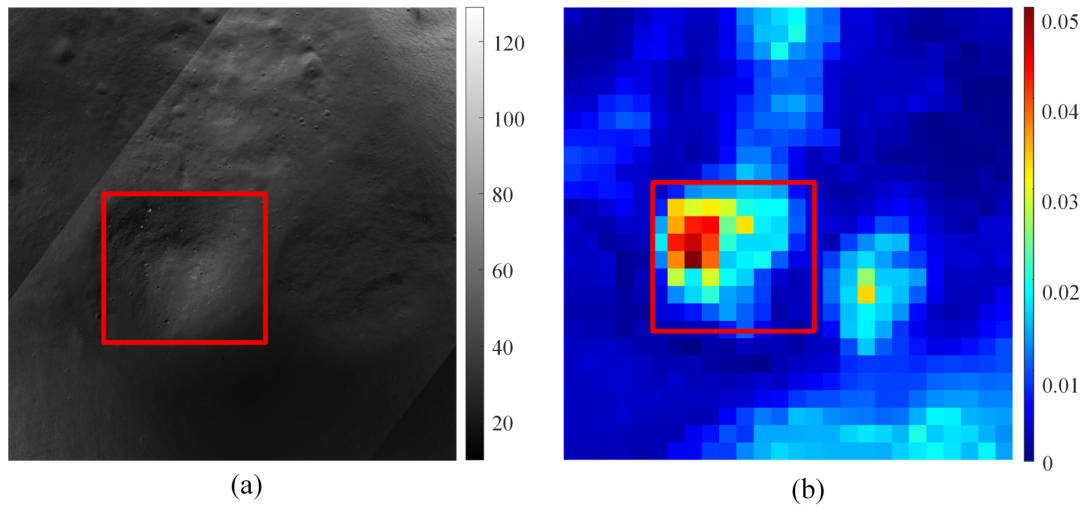
The spatial distribution and abundance of surface rocks on the Moon serve as critical determinants in landing site selection, mission planning, and scientific investigations. Due to the lack of optical and thermal infrared observations in permanently shadowed region, conventional remote sensing techniques encounter substantial challenges in directly retrieving rock-related information from these areas. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) penetrates the lunar regolith, providing a robust and reliable means of acquiring subsurface information, particularly under rugged terrain or low-illumination conditions. This study proposes a rock abundance retrieval method by integrating Mini-RF SAR and Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter digital elevation model (DEM) data with a machine learning framework. Feature parameters are extracted from the SAR and the DEM data, and a random forest model optimized by the sparrow search algorithm is constructed to estimate rock abundance in lunar maria regions. Model training and validation in representative lunar maria areas demonstrate high predictive accuracy, with a coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.77 and a root mean square error of 0.004. The predicted rock abundance shows strong agreement with measurements from the Diviner thermal radiometer, supporting the model’s reliability. Furthermore, the trained model is applied to selected permanently shadowed regions near the lunar south pole, where optical remote sensing is unavailable due to the lack of sunlight. In these challenging environments, SAR and DEM data provide essential observational support for rock abundance estimation. This approach represents a viable pathway for investigating rock distribution in polar regions, and provides essential data and methodological insights for future lunar exploration, particularly regarding landing site safety and in-situ resource evaluation. [pdf, SCI, IF=2.8000, CAS-G3, JCR-Q2]
Recommended citation:
Z. Guo, Z. Song, C. Li, G. Shu*, and N. Li, “An SSA–RF-based Lunar Surface Rock Abundance Retrieval Method Using Multi-source Remote Sensing Data,” in Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 025005, Dec. 2025, DOI: 10.1088/1674-4527/ae2103.
bibtex:
@ARTICLE{Guo2025SLunarSurfaceRARetrieval,
author={Zhiyuan Guo and Zhaobo Song and Chenya Li and Gaofeng Shu and Ning Li},
journal = {Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics},
title={An SSA–RF-based Lunar Surface Rock Abundance Retrieval Method Using Multi-source Remote Sensing Data},
year={2025},
volume={26},
number={2},
pages={025005},
doi={10.1088/1674-4527/ae2103}
}